Advancing Inflammatory Bowel Disease Research with Humanized Mouse Models
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) represents a complex spectrum of gastrointestinal disorders that globally afflict millions. The intricate interplay of genetic and environmental factors culminates in chronic immune system dysregulation in the gastrointestinal tract. This dysregulation triggers aggressive inflammatory responses that the immune system fails to suppress, in response to normal enteric flora. The most prevalent forms of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, and existing drug treatments often fall short in efficacy and can entail negative side effects.
To enhance our understanding of IBD and explore more effective treatments, animal models, particularly mice, are indispensable tools for elucidating the underlying mechanisms and for evaluating potential therapeutic options. TransCure bioServices has developed two such models: the dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) model, which emulates ulcerative colitis, and the 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) model, which mirrors Crohn’s disease.
Make sure to check out our complimentary webinar “Why Use Humanized Mouse Models for Translational Studies in Inflammatory Disorders?“, a 2 minute introduction is provided here.
DSS Model in Humanized Mice
The DSS model, frequently used to simulate ulcerative colitis, involves administering DSS in the drinking water of humanized mice. This exposure leads to damage to the colonic epithelial cell monolayer, triggering the invasion of bacteria and related antigens into the mucosa, which in turn induces the secretion of human pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 or TNF-alpha. The mice models can present a spectrum of responses, including acute colitis, chronic colitis, or colitis-induced dysplastic lesions, depending on varying factors.
During the course of the study, several parameters are evaluated:
- Global clinical score: Body weight loss, diarrhea, bleeding
- PD analysis by Flow Cytometry
- Thickening of the colon, change in the vascular pattern, fibrin deposit, granularity of the mucosal surface (these parameters are scored by endoscopy)
- Colon shortening
- Colon infiltration/inflammation by IHC and/or Flow Cytometry
Our team’s contributions to a collaborative study with PMI, “Tobacco Alkaloid Assessment in a DSS-Induced Colitis Mouse Model with a Fully Humanized Immune System,” published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences in March 2023, illuminates the potential of tobacco alkaloids as anti-inflammatory treatments for IBD. The research revealed that nicotine significantly mitigated colitis symptoms, including inflammation and tissue damage, while anatabine exhibited comparable efficacy trends. This study provides a very good example of the power of humanized mice to predict the efficacy of a treatment in patients.
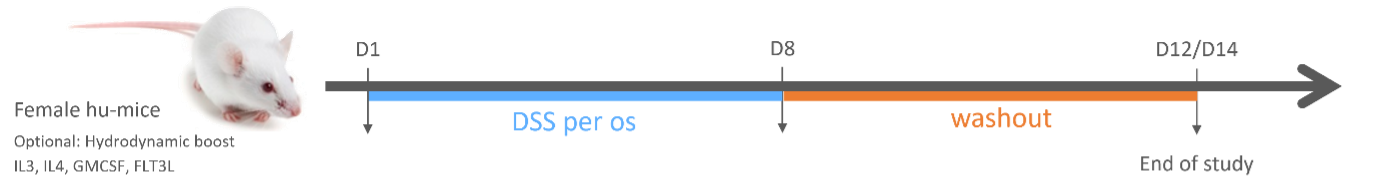
DSS-Acute Inflammation – Experimental Design
Figure 1: Experimental design of DSS-acute induction; D1: First day 1 of DSS induction
The acute model of IBD follows a precise schedule. From day 1 to day 7, we introduce DSS solution to the mice’s drinking bottles. The period from day 8 to day 12 serves as a wash-out phase, where we replace the DSS solution with water. The termination of the acute model can be set between days 11 and 13 post-induction, subject to the health status of the animals. Typically, treatments start prior DSS administration. Humira (Anti-TNF-alpha) and Cyclosporine-A can be used as positive control.
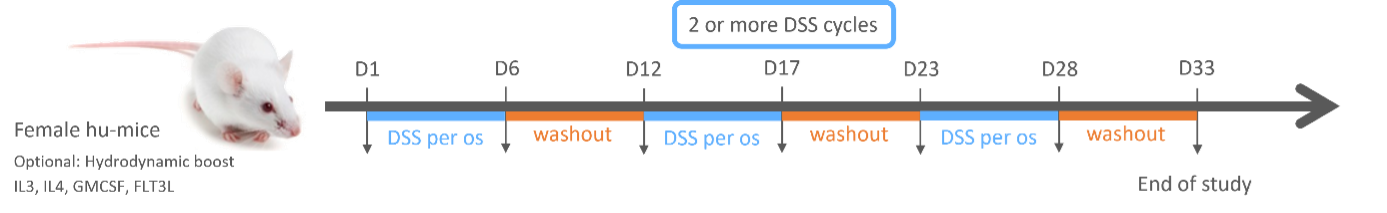
DSS-Chronic Inflammation – Experimental Design
Figure 2: Experimental design of DSS chronic induction; D1: First day 1 of DSS induction
The protocol for the chronic IBD model involves three distinct cycles of DSS administration, each serving to perpetuate a chronic condition of IBD. The first cycle initiates on Day 1, with subsequent cycles commencing on Days 12 and 23. From Day 1 through Day 27, we provide the animals with the DSS solution in their water bottles. A wash-out period starts from Day 7 and extends to Day 33, during which we substitute the DSS solution with water until the cycle concludes. The chronic model can be terminated between Days 31 and 35, depending on the health of the animals and the client’s specific needs. Typically, treatments start a few days following DSS induction. Humira (Anti-TNF-alpha) and Cyclosporine-A can be used as positive control.
TNBS-Induced Mouse Model for Colitis
The TNBS mouse model initiates colitis via the intra-rectal administration of TNBS, a hapten agent, dissolved in ethanol. This procedure, involving a single TNBS dose, triggers acute inflammation specifically in the distal portion of the colon. The critical role of CD4+ T cells bearing a Th1 profile in the onset of colitis underscores the relevance of this model to human conditions.
The mechanism involves ethanol disrupting the epithelial barrier, which facilitates TNBS binding to mucosal proteins. This binding renders the proteins immunogenic, setting them up for processing by antigen-presenting cells in the lamina propria. The subsequent reaction triggers an excessive IL-12 secretion by macrophages, inducing a robust Th1-pro-inflammatory immune response.
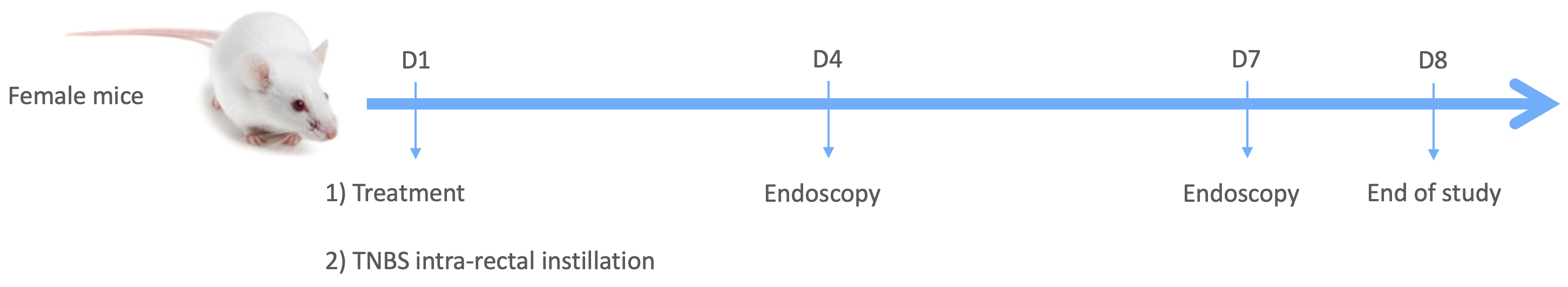
TNBS – Experimental Design
Figure 3: Experimental Design of TNBS induction
On Day 1, mice are treated with TNBS, co-administered with ethanol, via the intrarectal route under anesthesia. Without further TNBS exposure, inflammation persists for a few days, with peak symptoms observed around Day 4. Due to this short duration, we recommend initiating treatments on the day of TNBS administration. As a reference, anti-human-IL12 treatment (Ustekinumab) can be used, which should be administered a few hours before TNBS instillation.
DSS vs TNBS Chemically Induced
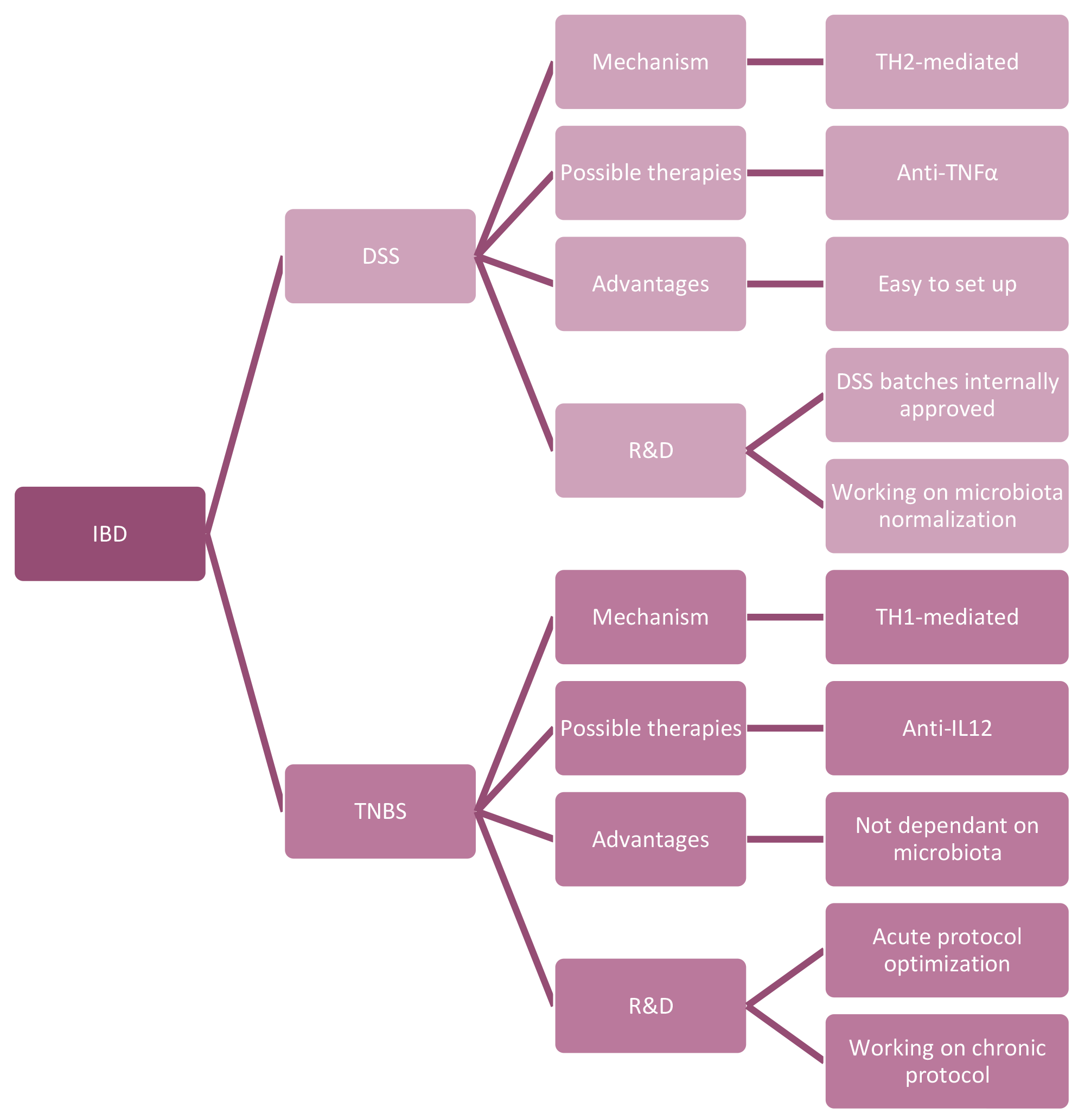
CD34+ humanized mice are an optimal choice to study IBD disease and to evaluate the immune, therapeutic, and toxicological properties of molecules targeting human immune cell infiltration, human cytokines expression, or complex interactions with the microbiota. With more than 10 years of expertise in CD34+ humanized mice and in IBD studies, TransCure bioServices can guide you through these models and provide the most effective solutions tailored to your needs.
Interested to know more? Do not hesitate to contact us!